Logic in Computer Science (GEWINN InfoDay 2018)
| DATE: | Wednesday, November 14, 2018 |
| VENUE: | Messe Congress Center, Messeplatz 1, 1021 |
The report in German on the TU Wien website here
The VCLA has attended the GEWINN InfoDay, a congress that is yearly attended by more than 6000 pupils aged 16 and above. The congress took place on November 16, 2018, in Vienna.
The congress program consisted of seminars of high-level speakers such as the Austrian head of the government Sebastian Kurz, and nearly 60 exhibitors from the government, research and teaching institutions, expert associations, and forward-looking businesses.
The VCLA has joined the congress under the umbrella of the TU Wien, and was part of the exhibition booth named “ICT Innovations”. Because the research groups hosting the VCLA are using logic as a tool that enables computer programs to reason about the world, the VCLA presented the participating pupils an example of this powerful tool which is called logic – a logic puzzle. The puzzle was designed originally by Maarten Löffler, University of Utrecht.
Next to the VCLA of TU Wien booth, the exhibition space provided information and interactive presentation of the current research and outreach activities of:
- ÖCG (Austrian Computer Association): Coding, Robotik (EDLRIS – European Certificate for Robots and Intelligent Systems) and 3-D Printing;
- Dimension Data: Videoconferencing Wall
- Barracuda: Visualisation of Data Protection und Firewalls
- OVE (Austrian Electrotechnical Association) and GMAR (Austrian Society for measuring, automation and robot technology)
- Technische Universität Wien (TU Wien): Logic in Computer Science and iMooX (Austrian university MOOC platform)
Logic in Computer Science
Even though people rarely have to mathematically prove things in real life, we are using logic anyway. We use it when we discuss plans for the next vacation, politics, when playing games, or when working. We get wrong results of our logical thinking when we are using made-up techniques. The need to think more clearly in modern life can be satisfied with training in logic.
Logic is a powerful reasoning tool. Originally invented as an aid for sound argumentation, it reached maturity in the form of mathematical logic and analytic philosophy in the early 20th century, with significant contributions from Vienna. At the Faculty of Informatics, TU Wien, the researchers are using logic as a tool that enables computer programs to reason about the world.
In three research areas of logic, a particularly good international visibility has been achieved in the last two decades. The first area is “Computational Logic”, especially proof theory, complexity theory, and automatic reasoning. The second area is the application of logic to “Databases and Artificial Intelligence”. The third area is “Computer Aided Verification” or “Model Checking”, where computer programs are used to examine algorithms for errors.
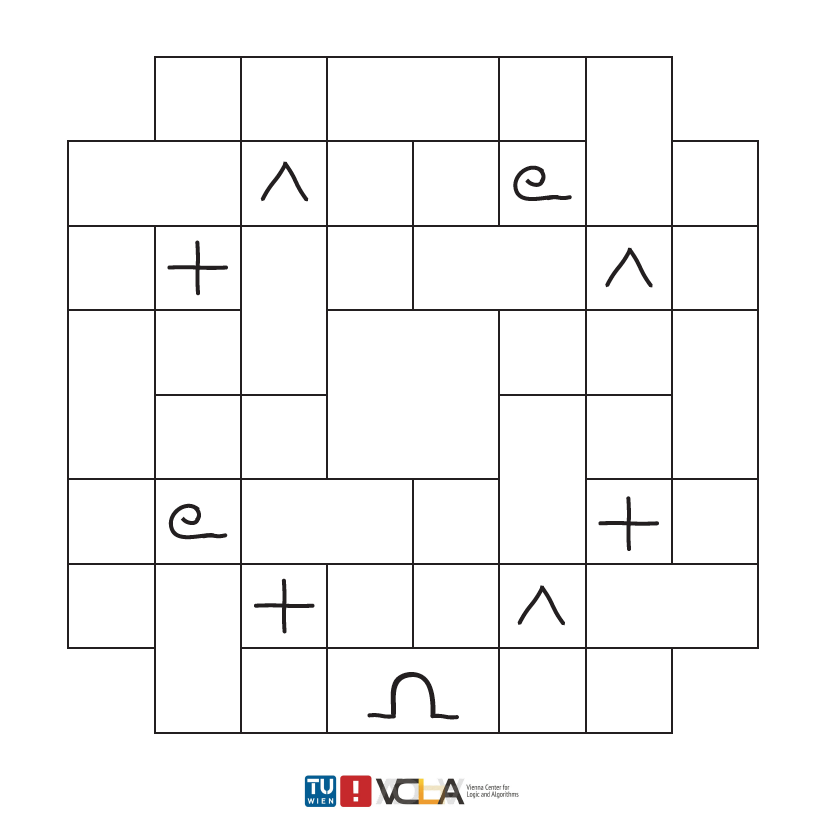
Logic Puzzle
Your task: fill in the grid with the four alchemical symbols for earth, fire, water, and air, such that the same symbols never touch each other, not even diagonally, by putting exactly one symbol in each rectangle, no matter the size of the rectangle.
Designed by the VCLA guest, Maarten Löffler, University of Utrecht. Want to enjoy more puzzles? Visit Löffler´s website here.
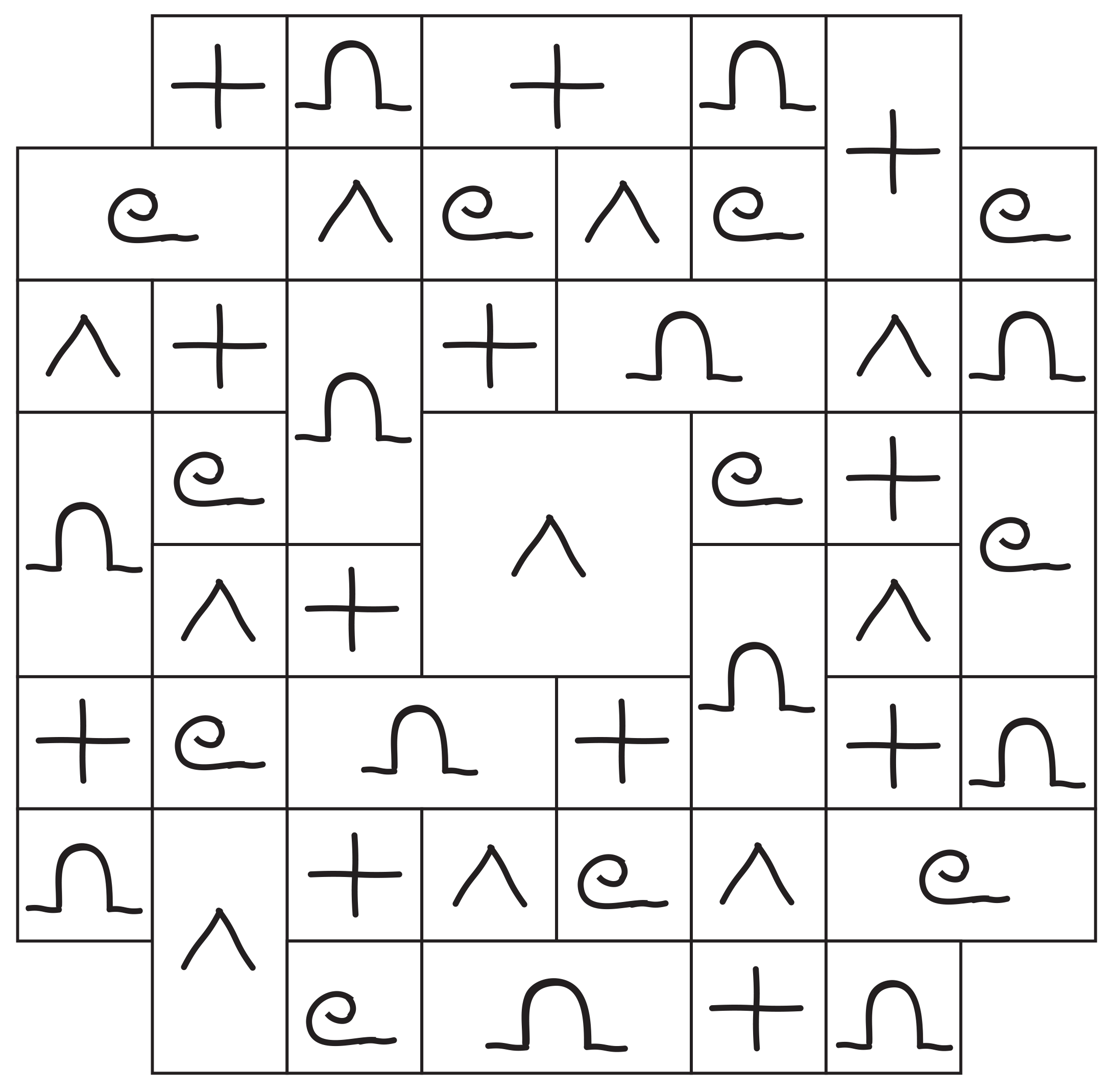
Solution
iMooX: Learn how to code, develop a start-up, or teach informatics
Professors from Faculty of Informatics, TU Wien, are also engaged in design of free courses for the first and only Austrian MOOC platform – iMooX. A MOOC (Massive Open Online Course) is a special form of an online course that combines traditional forms of knowledge such as videos, reading the material and problem-solving with forum discussions between teachers and students and quizzes which allow participants to monitor the acquisition of knowledge. MOOCs are optimal to convey knowledge to a large number of people wherever and whenever. There is no limit concerning the number of participants. Generally spoken, MOOCs present a low-barrier access to scientifically based information because of their multimedia format.
Using iMooX in the classroom
Contrary to the US competitors, all iMooX learning materials are not only free of charge but can also be reused. This concept is based on the so-called Creative Commons licenses meaning that the whole content offered on iMooX can be used for own (teaching) purposes and can also be reused free of charge.
Individual Programing with processing?
Program your own games or animations from the scratch with free iMOOx course designed by the team around Prof. Gerald Futschek. Visit the German course here.
Computer Science without a computer?
Additional resources for fostering of computational thinking, with examples of human sorting network are available here.
Videos of the nation-wide competition where pupils explain algorithms in 60 seconds here.
Photo Gallery
 |
 |
 |